Today the round 2 of the Community Evaluation Program for System Center Configuration Manager 2012 started again with the overview. The first run of the sessions was based on the beta 1 version, the round 2 will be based on the beta 2 version of SCCM 2012.
To keep all the members of the CEP interested, the setup of the sessions will be changed. In the first half of the session Jeff Wettlaufer will interview one of the engineers of the Configuration Manager team and highlight the changes in the beta 2 version. The second half of the session will be the slide deck, questions and demos. This session is still in the old format.
The overview session are highlights of the new and better features in SCCM 2012, in this blog I will write down the highlights of the session 🙂 Some features are already mentioned in one of the earlier CEP summery blogs.
System and User-centric
SCCM 2007 was fully optimized for Systems Management scenarios. Managing users in SCCM 2007 was a big challenge, the relation of users and the device or platform is always a hassle. SCCM will be System and User-centric:
- Still committed and focused on System Management scenarios
- Embrace User Centric scenarios:
- Moving to state based design, for Applications, Deployments and contents on the Distribution Points
- Full application life cycle model.
- Install
- Revision Management (new versions)
- Supersedence
- Uninstall
- Understand and intelligently target the relationships between user systems
- Management solution tailored for applications
- Administration promises:
- Let the administrator think; “User first”
- Deploy applications to users
- Manage users beyond the desktop
- ConfigMgr maintains the relationship between users and systems to solve core user targeting
- Set conditions to control installations
- Schedule “pre-deploy” to users’ primary devices for WoL, off hours, workgroups etc
- ConfigMgr will remember the relationship between the user and their applications
- Application Model captures administrative intent.
- Let the administrator think; “User first”
Application Model
The application model in SCCM 2012 is changed, an application can have more deployment methods. Deployment methods like MSI, app-v and mobile devices. The following points highlights the new application model:
- Manage applications; not scripts
- Application Management:
- Detection method – re-evaluated for presence:
- Required application (reinstall if missing)
- Prohibited application (uninstall if detected)
- Requirement rules – evaluated at installation time to ensure the application only installs in places it can, and should.
- Dependencies – relationships with other applications that are all evaluated prior to installing anything
- Supersedence – relationships with other applications that should be uninstalled prior to installing anything
- Update an application – automatic revision management
- Detection method – re-evaluated for presence:
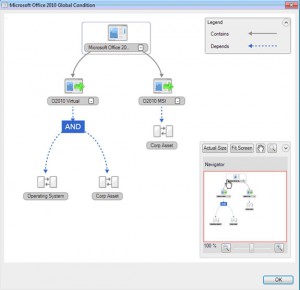 Application dependencies
Application dependencies
User Centric OS DeploymentSupport for new software distribution features during operating system deployment. Via requirement rules, dependencies and supersedence applications for a user can be installed during the OS Deployment. Via User Device Affinity support applications can be deployed to the primary user of a device or system.
The software Catalog in beta2 is enhanced and customizable so you can create your own logo’s and house style. The user can define work hours and new is the presentation mode. If the system is in Presentation Mode, deployments are suspended and baloon popups are suppressed.
Role-Based Administration
Role-Based Administration is SCCM 2012 has become mature. SCCM 2012 brings us 14 out of the box security roles. As an administrator you can create as much as roles as you like. Assigning roles to people will remove clutter from the console, since it supports “Show me what’s relevant to me” based on Security Role and Scope.
The out of the box security roles in SCCM 2012 Beta2 are:
- Application Administrator Role
- Application Deployment Role
- Application Editor Role
- Asset Analyst Role
- Asset Management Role
- Compliance Settings Management Role
- Full Administrator
- Infrastructure Administrator
- Limited Administrator
- Mobile Device Analyst Role
- Operating System Deployment Management Role
- Read-only Role
- Remote Tools Role
- Software Updates Management Role
Infrastructure
- Modernizing architecture
- Minimize infrastructure for remote offices
- Consolidating infrastructure for primary sites
- Scalability and data latency improvements
- Central Administration Site is just for administration and reporting, other work is distributed to the primaries as much as possible
- System generated data (HW Inventory and Status) can be configured to flow to CAS directly
- File processing occurs once at the primary site and uses replication to reach other sites (no more reprocessing at each site in the hierarchy)
- Be trustworthy
- Replace cumbersome object replication and cost associated to troubleshooting
- Utilizing core SQL engine technologies which simplify troubleshooting and reduce operational costs.
- When do I need a primary Site?
- To manage many clients.
- Add more primary sites for:
- Scale (more than 100.000 clients)
- Reduce impact for primary site failure
- Local point of connectivity for administration
- Political reasons
- Content regulation
- You can reduce primary sites:
- Decentralized administration: Role Based Administration
- Logical data segmentation: Role Based Administration
- Client Settings: Client settings for the hierarchy and unique collections
- Language: Language packs
- Content routing for deep hierarchies: Secondary sites or Distribution Points
- One Distribution Point
- PXE Service Point – increased scalability beyond the old limit of 75 PXE service points per site
- Multicast option
- Throttling and scheduling to that location
- Pre-stage of content and specify drives for storage
- Improved Distribution Point Groups
- Manage content distribution to individual Distribution Points or Groups
- Content automatically added or remove from Distribution Points based on Group membership
- Associate Distribution Point Groups with collections to automate content staging for software targeting to the collections
- No Branch Distribution Points anymore. Distribution Points can be installed on clients and servers.
- Boundaries
- Boundaries represent network topology used to optimize the network utilization
- Clients use boundaries to:
- Automatically determine site assignment
- Locate the best Management Point
- Locate the best Distribution Point or State Migration Point
- Define separate boundaries for client activities versus content
- Automatically create boundaries with the Forest Discovery method:
- Discovers AD sites, IP Subnets, IPv6 Prefix Type boundaries and will support supernetting
- Can automatically add them as boundaries
- Can discover boundaries and allow you to add them later
- Boundaries are members of one or more groups;
- Groups support: site assignment, site system look ups or both
- Create group with boundaries in one step
- Add boundaries to an existing group
- Multi select and reflective views supported
- Groups simplify administration of 100’s or 1000’s of boundaries
- Client activity and health
- Out of the box health and remediation solution
- Server side metrics for evaluation client activity
- Policy request
- Hardware and Software inventory
- Heartbeat DDRs
- Status Messages
- Client Side monitoring / remediation for:
- Dependent Windows components and services
- ConfigMgr Client prerequisites
- WMI Repository and name space evaluation
- Inconsole en web reporting
- In console alerts when healthy / unhealthy ratio
Operating System Deployment
- Offline servicing of images
- Support for Component Based Servicing compatible updates
- Uses updates already approved in Software Updates
- Boot Media Updates
- Hierarchy wide boot media (no longer need one per site)
- Unattended boot media mode
- Use pre-executing hooks to automatically select a task sequence
- USMT 4.0
- USMT 4.0 is configurable via the integration in the Management Console. It supports hard-link. offline and shadow copy features
Power Management
The new SCCM 2007R3 Power Management feature will also be available in SCCM 2012.
Settings Management
- Unified settings management across servers, desktops and mobile devices
- ConfigMrg 2007 reports configuration drift – ConfigMgr 2012 can set for Registry, WMI and Script-Based
- Improved functionality:
- Copy settings
- Define compliance SLAs for baselines to trigger console alerts
- Richer reporting to include troubleshooting, conflict, remediation information
- Enhanced versioning and audit tracking
- Ability to specify specifiv versions to be used in baselines
- Audit tracking includes who changed what
Remote control
Is back 🙂 With the SMS 2003 version of remote control there was a “big security leak” when the connection with a remote session was broken the desktop session was held open and accessible to other people.
The new version is more secure and better than the feature in SMS 2003.
Left out because of earlier blogs:
- Device Management
- Collection Management
- Software Updates
- Migration
The RTM of SCSM 2012 is still planned for Q4 of this year.


